Kafka triggers
Windmill can connect to Kafka brokers servers and trigger runnables (scripts, flows) when a message is received. Listening is done from the servers, so it doesn't take up any workers. Kafka triggers is a self-hosted Enterprise feature.
Kafka resource configuration
Before creating a Kafka trigger, you need to set up a Kafka resource. Head to the Resources page, click "Add resource" and select kafka.
The resource requires:
- Brokers: List of broker hostnames in the format
hostname:port - Security: Authentication and encryption settings
Security options
| Security mode | Description |
|---|---|
| PLAINTEXT | No authentication or encryption. Use only for development. |
| SASL_PLAINTEXT | Username/password authentication without encryption. Supports PLAIN, SCRAM-SHA-256, SCRAM-SHA-512 mechanisms. |
| SSL | TLS encryption with optional client certificate authentication. |
| SASL_SSL | Username/password authentication with TLS encryption. |
| SASL_GSSAPI | Kerberos (GSSAPI) authentication without encryption. |
| SASL_SSL_GSSAPI | Kerberos (GSSAPI) authentication with TLS encryption. |
Kerberos (GSSAPI) authentication
For enterprise environments using Kerberos, select SASL_GSSAPI or SASL_SSL_GSSAPI security mode.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| kerberos_service_name | Kerberos principal name of the Kafka broker service (default: kafka) | No |
| kerberos_principal | Client's Kerberos principal (e.g., user@REALM.COM) | Yes |
| keytab_path | Path to keytab file mounted on the worker | No* |
| keytab_base64 | Base64-encoded keytab content | No* |
*Either keytab_path or keytab_base64 must be provided.
Using keytab_base64: Encode your keytab file with base64 -w0 /path/to/keytab and paste the result. This is stored securely and written to a temporary file at runtime.
Using keytab_path: Mount the keytab file on the worker container and provide the path. This is useful when deploying with Kubernetes secrets or Docker volumes.
Ensure the worker has access to a valid /etc/krb5.conf file with the correct realm configuration. When using SASL_SSL_GSSAPI, you can also provide CA certificates for TLS verification.
How to use
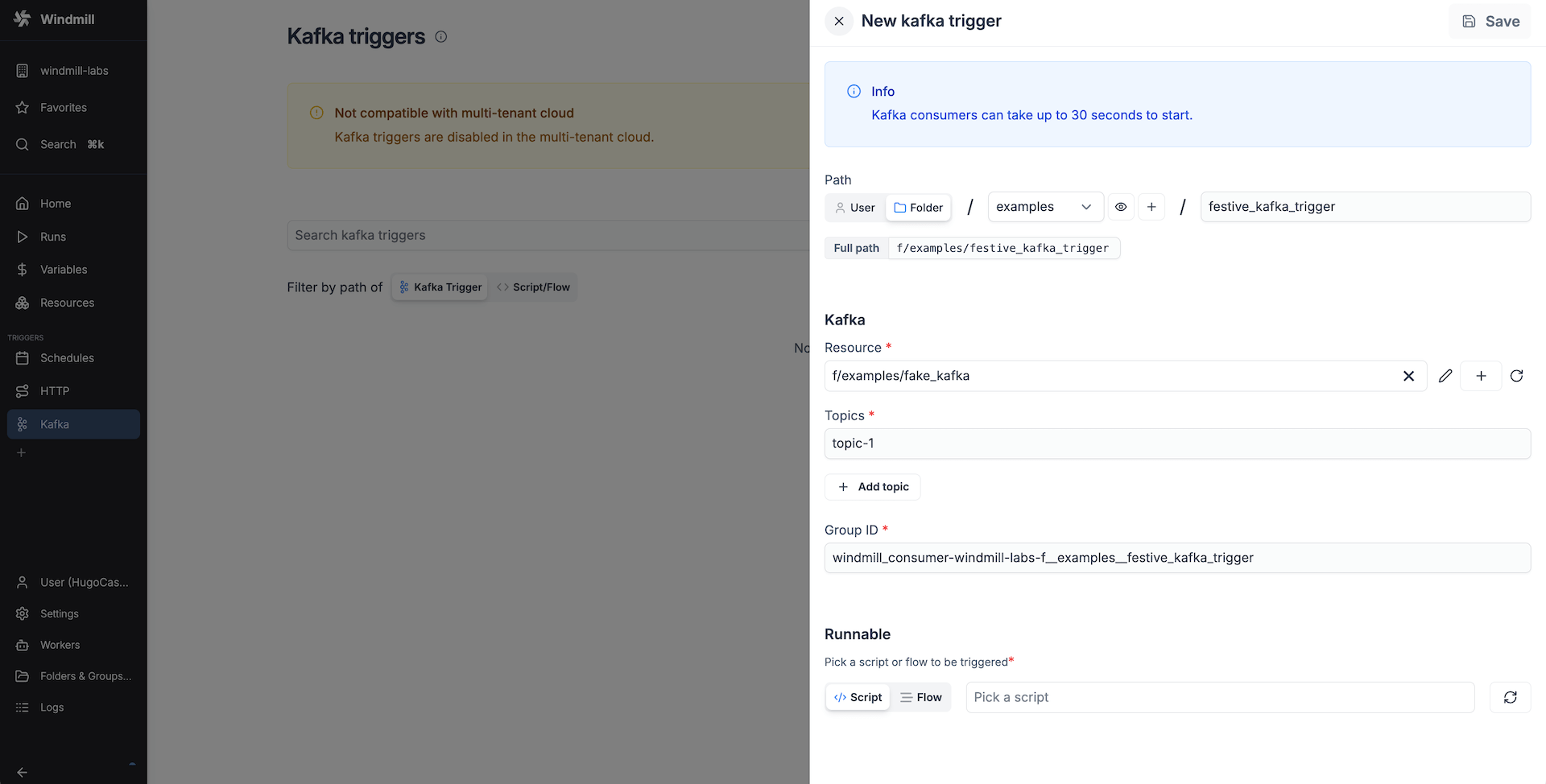
Create a new trigger on the Kafka triggers page. Add a Kafka resource with the broker hostnames (hostname:port) and the security settings. Specify the topics the trigger should listen to. The group id is automatically filled in from the current workspace and the trigger path. You can change it if necessary. It indicates the consumer group to which the trigger belongs. This garantees that even if the trigger stops listening for a while, it will receive the messages it missed when it starts listening again.
Once the Kafka resource and settings are set, select the runnable that should be triggered by this trigger.
The received webhook base64 encoded payload will be passed to the runnable as a string argument called payload.
Here's an example script:
export async function main(payload: string) {
// do something with the message
}
And if you use a preprocessor, the script could look like this:
export async function preprocessor(
event: {
kind: "kafka",
payload: string, // base64 encoded payload
brokers: string[];
topic: string; // the specific topic the message was received from
group_id: string;
}
) {
if (event.kind !== "kafka") {
throw new Error(`Expected a kafka event`);
}
// assuming the message is a JSON object
const msg = JSON.parse(atob(event.payload));
// define args for the main function
// let's assume we want to use the message content and the topic
return {
message_content: msg.content,
topic: event.topic
};
}
export async function main(message_content: string, topic: string) {
// do something with the message content and topic
}
Error handling
Kafka triggers support local error handlers that override workspace error handlers for specific triggers. See the error handling documentation for configuration details and examples.